Need Support? Call Us!
858-571-3154
10 Security Checkups Every Small Business Should Do at the Start of the New Year
How to Tell If an Email Is Legitimate or a Phishing Scam
How to Tell If an Email Is Legitimate or a Phishing Scam
In today’s digital age, email has become a vital communication tool for both personal and professional interactions. However, it has also become a preferred channel for cybercriminals looking to exploit unsuspecting users through phishing scams. These fraudulent emails are designed to trick recipients into divulging sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details or other personal data. It is essential to know how to identify phishing emails to avoid falling victim to them. Here are some key tips to help you distinguish between legitimate emails and phishing attempts.
Check the Sender’s Email Address
One of the first red flags in a phishing email is the sender’s email address. While the sender’s name might look familiar, the actual email address may not match the legitimate domain. Scammers often use addresses that look like official ones but with slight alterations. For example, instead of a legitimate domain like “@amazon.com,” a phishing email might come from “@amaz0n.com” with a zero replacing the “o.” Always double-check the email address for any subtle differences. If the address doesn’t match what you expect from the sender, it’s a good sign the email might be a phishing attempt.
Look for Generic Greetings
Legitimate companies that you’ve interacted with typically use personalized greetings in their communications. If an email starts with “Dear Customer,” “Hello User,” or other vague language instead of addressing you by your actual name, it’s a red flag. Phishing scams often use generic greetings because they send out mass emails to as many people as possible, hoping a few will fall for the trap. A legitimate email from your bank or a service provider will likely use your full name or account information to confirm authenticity.
Examine the Content and Tone of the Email
Phishing emails often have a sense of urgency or use scare tactics to manipulate you into taking immediate action. They may claim that your account has been compromised, that there’s an urgent issue with your payment or that you need to verify your information to avoid suspension. Legitimate companies typically won’t ask for sensitive information (like your passwords or credit card details) directly through an email. Be cautious of any message that pressures you to click on a link or open an attachment urgently, especially if the request seems out of the ordinary.
Inspect the Links and Attachments
One of the most dangerous elements of a phishing email is its links or attachments. Before clicking on any link, hover over it to see the URL. A phishing link may look like a legitimate website at first glance, but if you inspect the full URL, you may notice it’s slightly altered or completely unrelated to the company. Similarly, avoid downloading attachments unless you are certain they are legitimate, as they can contain malicious software designed to steal your personal data or infect your device. If in doubt, visit the company’s website directly by typing the URL into your browser instead of clicking on a suspicious link.
Check for Poor Grammar and Spelling Mistakes
Reputable companies typically have teams of professionals ensuring that their emails are free from grammatical errors and spelling mistakes. Phishing emails, on the other hand, are often riddled with mistakes because they are sent out in bulk by scammers, sometimes from non-native English speakers. If an email is poorly written, lacks proper punctuation or contains strange phrasing it’s a good indicator that it could be a phishing scam. Take time to read the email carefully and look for inconsistencies that might give away its fraudulent nature.
Staying safe online requires a careful eye and a healthy dose of skepticism, especially when it comes to emails. By paying attention to the sender’s address, scrutinizing the greeting, inspecting the email’s content and being cautious about links and attachments, you can protect yourself from phishing scams. When in doubt, it’s always safer to contact the company directly through their official website or customer service to confirm the legitimacy of any communication. Being proactive and vigilant can help you avoid falling into the traps set by cybercriminals.
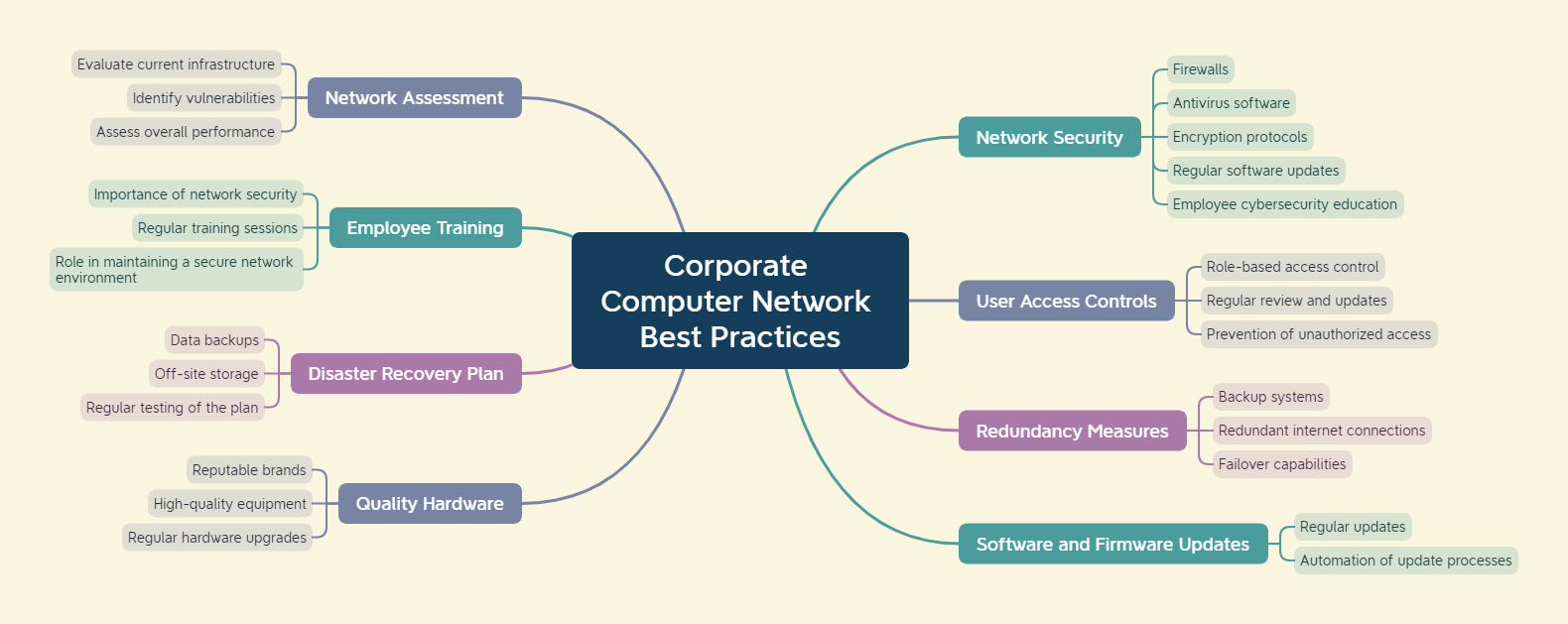
The Corporate Computer Network: Best Practices for Business Owners
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, a reliable and secure computer network is the backbone of any successful enterprise. Whether you’re a small startup or a well-established corporation, the effectiveness of your corporate computer network directly impacts productivity, collaboration, and overall business success. In this article, we’ll explore some general best practices for business owners to ensure they have a robust and secure computer network.
- Conduct a Network Assessment: Before implementing any changes or upgrades, it’s essential to conduct a thorough network assessment. This involves evaluating the current infrastructure, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and assessing overall performance. This initial step provides a solid foundation for planning improvements and helps prevent any unforeseen issues down the line.
- Prioritize Network Security: Security should be a top priority when managing a corporate computer network. Implementing robust security measures helps protect sensitive data, client information, and your company’s reputation. Utilize firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption protocols to safeguard against cyber threats. Regularly update and patch software to address potential vulnerabilities and ensure that employees are educated on cybersecurity best practices.
- Establish User Access Controls: Limiting access to sensitive data is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your network. Implement a role-based access control system that grants employees the appropriate level of access based on their responsibilities. Regularly review and update user permissions to align with organizational changes and to prevent unauthorized access.
- Implement Redundancy Measures: Minimize downtime and ensure business continuity by implementing redundancy measures. This includes backup systems, redundant internet connections, and failover capabilities. By having backup solutions in place, you can quickly recover from hardware failures, minimizing the impact on productivity.
- Regularly Update Software and Firmware: Outdated software and firmware can be a significant security risk. Regularly update all network devices, including routers, switches, and servers, to ensure they have the latest security patches and performance improvements. Automate update processes whenever possible to streamline this essential maintenance task.
- Invest in Quality Hardware: The quality of your network hardware directly influences its reliability and performance. Invest in reputable brands and high-quality equipment that can handle the demands of your business. Regularly upgrade hardware to keep pace with technological advancements and to ensure compatibility with the latest software.
- Implement a Disaster Recovery Plan: Prepare for unforeseen events by developing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan. This should include regular data backups, off-site storage solutions, and a step-by-step guide for restoring operations in the event of a disaster. Regularly test your disaster recovery plan to identify and address any potential shortcomings.
- Provide Employee Training: Educate your employees about the importance of network security and best practices. Human error is a common factor in security breaches, so a well-informed workforce is a critical line of defense. Conduct regular training sessions to keep employees updated on the latest security threats and ensure they understand their role in maintaining a secure network environment.
A well-managed corporate computer network is essential for business success in the digital age. By following these best practices, business owners can build a secure, reliable, and efficient network infrastructure that supports their organization’s growth and innovation. Regularly assess and update your network to stay ahead of emerging threats and technological advancements, ensuring that your business remains competitive and resilient in today’s dynamic business landscape.
If your company would like more information about Network Best Practices, would like a Free Network Assessment or how to keep your network running at its best, contact Infinity Networking today!
Cybersecurity and Ransomware – an Overview
IT professionals, like myself, live and breathe in a world of technical jargon and frequently toss out vague but dire warnings to the non-technical as if they should heed our expert advice without question. For their own good of course. But I have always believed that knowledge empowers us to make more informed decisions and it can only be of benefit when the non-technical have an understanding of these warnings. Business owners have a lot on their plates running their companies, dealing with day-to-day challenges and planning for financial success, but providing an overview of basic cybersecurity concepts and the threat of ransomware is something that all businesses should have some knowledge.
I had a client recently ask me to help them understand the basics of cybersecurity, what ransomware is and how to prevent it. There are stories almost every day about big companies, hospitals and government entities being affected by massive breaches in cybersecurity so it is no wonder that a small business owner may be asking, “Is my company’s network and data safe?” Following is a summary of these concepts and I have included some of the basic principles and explanations that hopefully may be more digestible by the non-technical minded.
–

Ransomware – the most dangerous cybersecurity threat to companies today.
The bad guys are not just targeting large businesses – their software is indiscriminate and can infect even a small 1 person company.
Ransomware usually infects a company through an unsuspecting email or a bad website. No antivirus or email filter is 100% effective so the last line of defense is the wariness of the end user. Security awareness training can help a company keep its employees informed and vigilant.
Prevention – All incoming email should be filtered by a good cloud-based scanning solution. Additionally, all workstations, laptops and servers should have active an antivirus application running. But do to the way these threats are triggered and spread, unfortunately many antivirus apps may not be as effective to prevent ransomware.
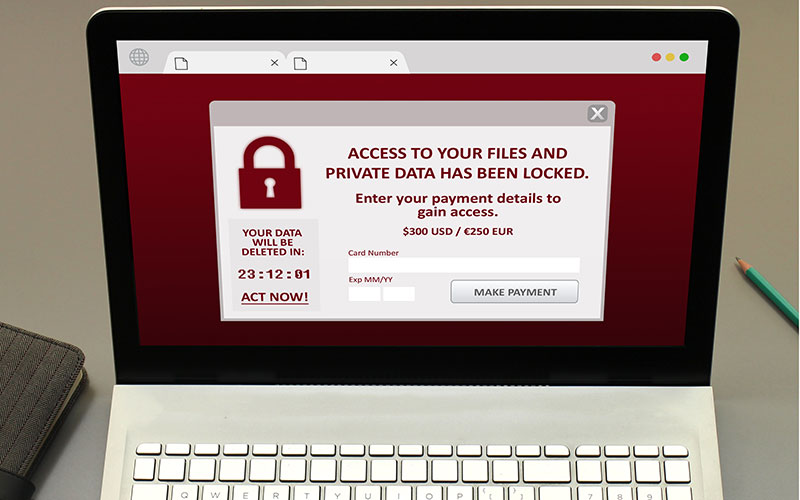
Detection – If an infection does occur, the first thing people will notice is that many shared files will not be able to be opened. Usually in the same folder, a file will appear that announces that the company’s files have been locked until a ransom is paid by bitcoin to a private bitcoin account (which is untraceable).
Ransomware can also infect emails and cloud-hosted files. The virus travels through network shares (drive letters) from the person’s machine to the server or cloud host and it can also access the user’s hosted emails and infect the whole company’s email database in the cloud.
Remediation – If a company falls victim to a ransomware infection, the first thing to do is either unplug the network cables from the infected machines or shut them down completely, especially the server(s). Sometimes it may be hard to tell where the infection started, so you may need to shut off all systems and bring them up one at a time to find the source.
At this point it would be a good idea to call a professional to help evaluate and take the next steps to recover from the infection. Depending on what backups are in place, the recovery can be easy, difficult or impossible. You may have heard about the impossible ones where the only seeming recourse is to pay the ransom (which should never be paid, in our opinion).
However, with good backups, especially backups with built-in ransomware detection, you can recover from a ransomware infection within hours if not minutes. Good backup solutions have algorithms that detect the traits of ransomware like mass changes to file contents or extensions or security and they shut down backup immediately so the infected files do not propagate to the cloud backups.
Here are three things you should ask yourself to get into the right mindset:
- Where is your data? Server, workstations, hosted email, cloud storage, laptops, personal machines offsite?
- Is this data backed up? How frequently?
- Are your employees trained to avoid suspicious emails?
Infinity Networking can assist companies to take effective steps to prevent, detect and counter ransomware attacks.
For more information on these preventative measures, including a good email filtering service like Barracuda Cloud Control or Webroot Security Awareness Training, contact Infinity Networking for a FREE TRIAL of these services.
Click here for more information about Infinity Networking’s Cybersecurity solutions
How to Avoid Phishing Scams
The most common way that business and personal accounts become compromised is through phishing and spear phishing attacks. These attacks are more common recently with the pandemic forcing people to work from home and often separated from their company’s established cybersecurity protocols. The majority of computers these days have some form of antivirus and firewall protection, but human nature is often the weakest link in the security wall. In this blog post, you will learn how to recognize a fake email and how to avoid becoming the victim of a phishing scam.
What is Phishing?
A phishing attack is an email sent by a bad actor that appears like a legitimate notice or request for information. Most of the time they appear as if they originate from Microsoft, Apple, a well-known bank, Paypal, Amazon, etc. The phishing email often announces a new feature or a request for the user’s information that requires the user to log into their account using their credentials. The links from these phishing emails lead to a very convincing (yet fake) website that appears legitimate. But when the user enters their information, the victim has essentially given the scammer their private credentials. There have been numerous high profile celebrities and politicians that have fallen for these scams.
—
The Impulsive Clicker
Most people, especially in a business environment, gets 10’s if not 100’s of new emails each day. We have become rather proficient at sorting through the spam and keeping the important ones. However, since we are dealing with a large volume of emails at one time it is easy to just open one from a familiar source and click on the link. Especially if the email is from a popular vendor or B2B company.
Phishing attacks take advantage of our human nature to be in a hurry and not carefully read what we are opening.
—
Advanced Tactics – Spear Phishing
Phishing attacks have now evolved into a more sophisticated form called ‘spear phishing’. Someone who receives an account password reset email from eBay, but who never uses eBay will know right away that the email is not legitimate. But if the scammers can get a little more information, for example the name of a co-worker at the company, they can send their phishing email that looks like it comes from someone familiar, bypassing that first line of mental defenses. The more the scammers know about a recipient; their co-workers, vendors, clients, account numbers, etc. the more convincing they can make the phishing emails appear. This is called spear phishing.
Phishing in Other Ponds
Phishing attacks are now common in other communication media as well including text messages, phone calls and search engines.
Arming Yourself
How do you avoid being the victim of a spear phishing attack? There are few tactics that everyone needs to know.
1) Slow down and stop being the ‘impulsive clicker’. Look at not only the sender’s name, but also the email address. At the top of the email, you will see the name of the person and then their email address between < and >. For example John Smith <[email protected]>. If the address looks like this John Smith <[email protected]> then that should raise a big red flag!
2) If you get an email that looks like it is from a well-known organization, look for misspellings and poor grammar. Also, use your mouse to hover over any hyperlinks (do not click on them). Most of the time, fraudulent links will be obvious when you look at their address in the bar at the bottom. See example below:
This is supposedly from the “Microsoft Account Team”. Notice the inconsistent capitalizations, the incorrect usage of ‘expired’ and the email address it is sent from – doesn’t look like Microsoft.
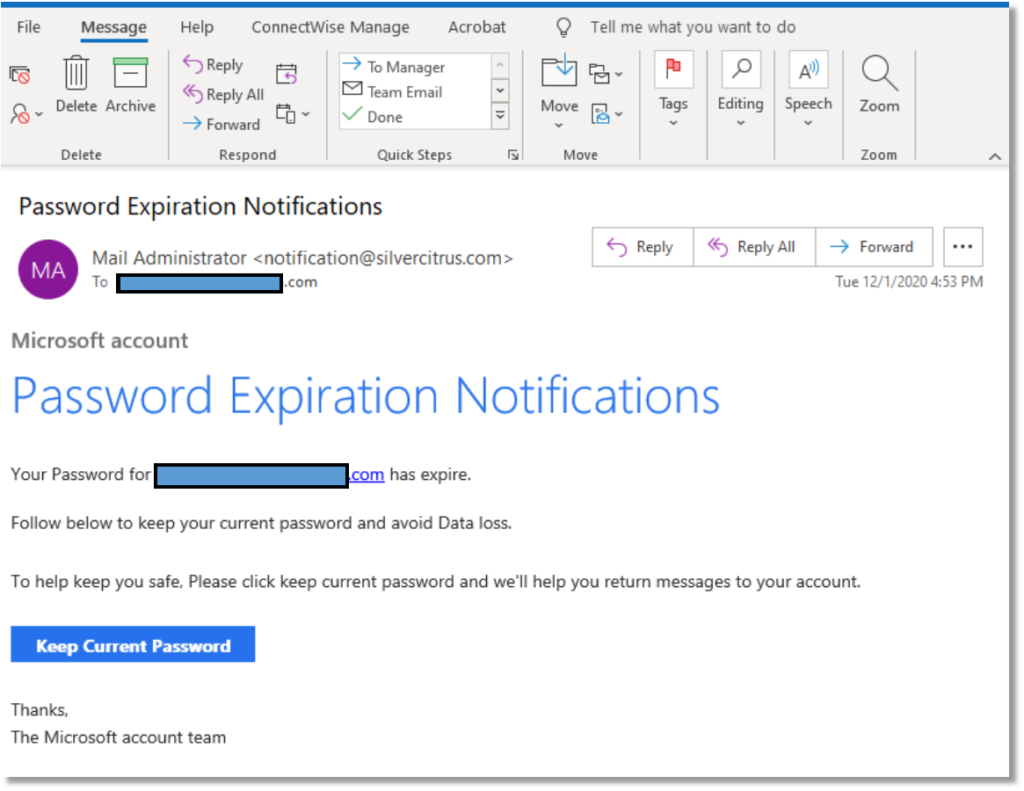
When the mouse is hovered over the “Keep Current Password” box, this is the link that appears:
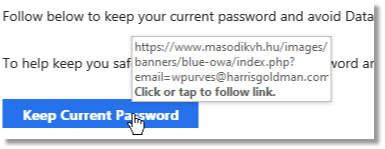
Doesn’t look like it directs to Microsoft…
3) Employing a robust enterprise-grade email filter is also a good way to avoid phishing attacks. Services like Barracuda Cloud Control have built-in mechanisms to block these types of scams.
4) One of the most effective IT security measures a company can make is to invest in regular Security Awareness Training. Almost all compliance regulations require companies to keep their employees updated and tested against the latest cyber threats on a regular basis.
For more information about what you can do to prevent a successful phishing attack, including a good email filtering service like Barracuda Cloud Control or regular Webroot Security Awareness Training, contact Infinity Networking for a FREE TRIAL of these services.
Click here for more information about Infinity Networking’s Cybersecurity solutions
—
Tips for Companies with Work-from-Home Employees
As the current global pandemic rolls along, most businesses are evaluating how they can continue to operate efficiently and successfully while keeping their employees safe. By now, many companies have allowed their employees to work from home, trying their best to stay in business.
Here are 6 helpful suggestions that businesses with work-from-home employees should consider:
Home Workspace
Just as a workplace provides a dedicated space for their employees; a cubicle, an office or some other area to set up a computer and spread out papers, the work-from-home employee needs a place to work as well. In the familiarity and comfort of their own homes, many employees may be working from their dining room table or the couch. Employees should be encouraged to try to set up their home workspace somewhere separated from the unavoidable sounds and distractions – preferably somewhere away from noisy televisions, family traffic and if possible, a room that has a closeable door. Of course, not everyone has this flexibility, but the more a work-at-home employee can emulate an office environment mindset, the more productive they will be.
Equipment
Few businesses have the ability to offer computers and peripherals for their employees to take home with them. Some workers have computers at home that they can use, but what if they don’t? Here are some options that employers may want to consider:
- Allow the employee to take home their work machine
- Purchase a refurbished workstation through a reputable vendor such as Dell for their work-at-home employees (https://www.dell.com/en-us/dfh/shop/dell-refurbished/cp/outlet)
- Lease a computer for the employee while the office is off-limits
- Headphones with a mic also help filter out extraneous noises
It is important that if a company wants their employees to be productive while working from home, they must ensure that they have adequate equipment to do their job.
Security
When an employee is working from home, there will be inherent security risks to mitigate. The easiest way to think about these security concerns is by using the three-fold ‘PPT’ model:
People – Who needs access to the company data, network and resources? And are those people trained to identify email phishing scams, securing their workstations with a password and not sharing their company access with other people?
Process – It may be helpful to have documented procedures for work-from-home employees; ensure they log out of their remote connections when they are not working, report any unusual emails or phone calls requesting access and have a go-to resource for any IT-related concerns or requests.
Technology – Besides a fully functioning workstation, remote workers should have a good antivirus and anti-malware solution. Do not assume that the employees’ home machines are protected or secure. If they are using their own equipment, it is especially important that the company require and possibly provide basic antivirus software for their employees. Having a trained IT professional evaluate and remediate the security of employees’ at-home workstations should be a part of any work-from-home strategy.
Accountability
Working from home is not like working in an office. There will inevitably be many interruptions, distractions and diversions that the employee will face on a daily basis. Realistically, it is very difficult to keep employees on task all day while they are not supervised, but accountability can be quantified if planned well. A manager or supervisor should evaluate the level of autonomy that they expect from their employees and work together to establish a reasonable set of goals per day, week or other timeframe. If the employee is meeting these predefined goals to the manager’s satisfaction, then accountability is easier to maintain.
There are a number of technology solutions to assist with accountability goals. Having a system to track daily and weekly tasks will not only keep the employee on target but will also allow the supervisor to review their progress throughout the timeframe. Here are some excellent tools to assist with task management:
1) Trello – a Kanban-style planning board which is effective in its simplicity and ease of use – and it’s free.
2) Google Workspace – good tool if your team uses Google’s online tools
3) Microsoft Teams – using the calendar and communication tools built into Teams will keep employers and employees on task throughout the day
4) Asana – project management for small teams with a free plan available
Video and Phone Tools
By now, most businesses have discovered that there are many options for video and phone conferencing. The most popular choices include Zoom, Teams and WebEx. If your company uses a conferencing tool such as these, here are a few helpful suggestions:
- Companies should be ready to assist their employees with the installation and use of video conferencing applications. This is new territory to many users and people may not have the technical ability to set these up on their own or know how to use them.
- Establish some basic ‘etiquette rules’ while using video conferencing. Most video conferencing applications monitor the microphones during a call and give preference to the ‘loudest’ voice. So remind users to take turns, be patient and only speak when they have something relevant to insert into the conversation.
- Encourage video conference users to be mindful of their surroundings. The camera picks up anything in its field of vision and the microphone amplifies sounds from the remote users’ environment. Users are better served by setting up their meetings in a room where the door can be closed and pets and children can be kept away.
Back to work plan, need office?
As companies are gearing up for an eventual return to the office, some may be considering whether they need to spend so much on office space if they can have capable remote users. Although the option is not ideal for all companies, there may be some advantage to have certain employees work from home either part-time or permanently. If a company is considering this arrangement, partnering with an experienced IT support company who has experience designing and implementing a remote workforce solution is highly recommended.
Infinity Networking can assist your company in creating an effective and secure work-from-home plan. Please Contact us today for more information.
Cybersecurity and Compliance is Important for All Companies
Cybersecurity and Compliance is Important for All Companies
If your company has regulatory compliance requirements, please read on. But even if it doesn’t – you should still read this.
What is IT Compliance?
IT Compliance means conforming to a set of rules, policies, standards or laws for your company’s specific industry for the protection of sensitive information and IT resources. Examples of which entities would require compliance include federal and state laws, industry regulations, contractual obligations and insurance policy requirements.
You may be surprised to know that all businesses are regulated. Besides the common regulations for HIPAA (medical record privacy) and PCI (credit card processing), all states have data breach notification laws. Many states also have laws protecting the private information of customers, including social security numbers, driver’s license numbers and credit card numbers.
You may think, “We do not collect any of that information so we have nothing to protect.” Are you sure? And can you prove it if your company was investigated? For example, there was a known case where a former CFO had created a spreadsheet of all the employees’ social security numbers and bank account numbers so he could easily access the information and not have to look them up one by one in a secured database. The current CFO did not do this, but the spreadsheet still existed on his workstation and even included the CEO’s personal information!
So even though your company may not have any particular regulatory laws or compliance standards that are mandated by industry, the confidence to declare and prove that your company does not have unsecured personal information is a valuable asset.
Law, Regulation or Framework
IT Compliance can be organized at three different levels.
Law – The most absolute of compliance regulations have been made into Laws (or Acts). Any industry governed by these laws must not only safeguard their sensitive data, but must also be able to prove that the data is secure and that they are actively and proactively ensuring that their data is secure. Examples of regulatory laws include HIPAA (healthcare), GLBA (financial), FISMA (federal agencies), CCPA (California consumers), SOX (corporate governance), ITAR (US defense sales and services)
Rules – Although not laws, many industries have strict rules that they must adhere to and in most cases require independent audit and certification. Examples of industry rules include PCI-DSS (credit card privacy), DFARS and CMMC (US defense industry), FDIC (banking), HIPAA Security Rule (electronic health industry privacy), Title 21 CFR Part 11 (electronic records/signatures for biotech)
Frameworks – Neither laws, nor rules, frameworks are broad (and detailed) scopes of IT security concepts that many industries outline and define to assist with creating effective IT policies and procedures to secure data and IT systems. Examples of frameworks include NIST CSF (cybersecurity framework), NIST 800-53 (US federal information system privacy controls), NIST 800-171 (controlled unclassified information for non-federal information systems), ISO 27001 (international standard for information security) and ITSM (security framework for IT service providers).
What does my company need to do?
All companies, whether or not they are governed by laws, rules or frameworks should give some basic thought to their own cybersecurity standards. Statistically, businesses of all sizes are being actively targeted by criminals or malicious entities. A proper cybersecurity plan includes three co-equal areas of security compliance:
- Policies (a written statement of the company’s general stance on IT-related subjects, such as passwords, internet access, backups, etc.)
- Procedures (more specific details about how things are performed, such as which backup or antivirus applications are implemented, how a terminated employee is offboarded, etc.)
- Evidence (how your company documents changes to policies and procedures or deviations, exceptions and violations of security)
How Infinity Networking can help your company
Here is a list of the ways we can help your company attain proper cybersecurity standards, maintain those standards and create ongoing assurances that your company’s IT security is working and up-to-date.
Get the Basics in Place
- Your company should have a good antivirus application installed on all workstations, laptops and servers
- Your servers and critical workstations should be backed up or imaged regularly and the backups should be tested on a regular basis
- All of the operating systems on your workstations and servers should have the latest security patches and service packs
- Your company’s network should have a commercial-grade firewall between it and the internet
- You should know who is accessing your network data and remove anyone who is not authorized
Infinity Networking’s Managed IT Services is a valuable asset for your company to maintain a healthy IT infrastructure. Get more information about Managed IT Services.
NIST CSF (Cybersecurity Framework)
The NIST CSF has been adopted and used by many agencies and organizations because of its high-level, streamlined approach to cybersecurity. The NIST CSF has five components:
- Identify – Hardware, software and data should be identified and located
- Protect – IT systems should be protected by firewalls, antivirus, backups, etc.
- Detect – IT systems should be scanned or audited regularly to find changes or intrusions
- Respond – There should be a procedure in place to respond to any security breaches or intrusions into an IT system and report/record the incident
- Recover – In the event of a breach of security or data loss, there should be a procedure in place to recover lost data and remedy any vulnerabilities
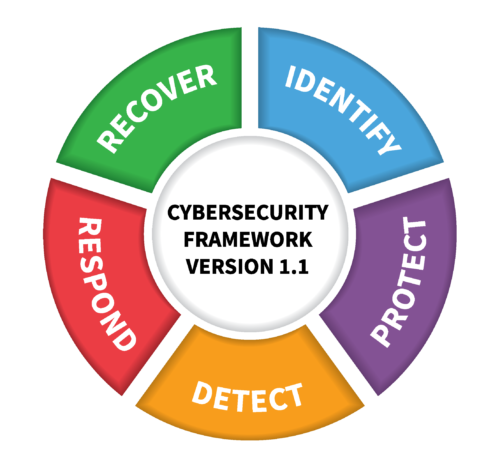
When all five of these components are properly addressed, a company can be assured that they have a strong foundation of effective cybersecurity policies and procedures.
Infinity Networking’s Network Security Assessment is based on the NIST CSF and will run an automated scan of your network’s resources to identify the security features you have enabled as well as any issues that should be addressed. We can also assist you in creating a remediation plan to fill the holes.
Specialized Compliance Standards
In addition to the general NIST CSF framework, Infinity Networking can also assist in the scanning, detection, remediation and documentation for more specific compliance requirements such as:
- CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification)
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- Cyber Insurance
- Microsoft Cloud Services (Office 365, Teams, SharePoint, OneDrive, Azure)
SPECIAL OFFER
If you would like a comprehensive, detailed security scan of your company’s network, including the identification of personally identifying information (PII), network security settings and external access testing, we are offering a one-time $300 service which includes the configuration and implementation of the network scan, the creation of customized reports and a detailed remediation plan to address any problems.
In addition, if you would like to have ongoing, monthly scans of your network or if you have a specific compliance requirement listed above, we will apply the one-time scan fee to your first month’s charges for our specialized Compliance Manager application. This service is installed at your location and automatically runs on a monthly basis, providing you with regular detailed reports that can be used as evidence for audits and requests for proof of compliance.
Please contact us if you have any questions, would like to see a demo or would like to view samples of the security reports. We can also discuss the next steps needed to implement a comprehensive Security Scan for your company.
The Greatest Threat to your Company’s Cybersecurity
The Greatest Threat to your Company’s Cybersecurity
No matter how much you have invested in your firewall or how effective your antivirus or anti-malware applications, you are still not protected from the most common means of intrusion by a hacker, virus or ransomware – YOU! (and your employees)
Nearly every news-worthy story of celebrities, high ranking government officials or well-established institutions have had their computers, accounts or networks compromised by the most insidious, common weakness – human nature. According to Webroot’s 2020 Cybersecurity Report, cybersecurity breaches will be increasing this year.
Just as allowing a stranger through your home’s front door is asking for trouble, opening an email from someone who seems legitimate can be just as dangerous. And the bad guys are getting much better at gaining your trust. There are two methods they use to fool you:
Phishing
Not too long ago, the bad guys would send batches of emails to random people and make the email look like it came from a bank or a well-known website like eBay or Amazon or Walmart. The email might inform the recipient that their password had expired or that their account had some suspicious activity. The email then requested that the user change their password through a link which asked for their old password and then to select a new one. However, these emails did not come from a legitimate source and the website, which looked very legitimate, collected their credentials and stored it for future abuse. These poor victims had been ‘phished’.
Due to news reports and better cybersecurity awareness, the average computer user started to become more aware of these attempts to steal their information and credentials, so the bad guys had to change their tactic slightly.
Spear Phishing
When you receive an email, one of the first things you look at is the sender. Is it from someone I know? Maybe a relative or a coworker? Is it from a business or website that I use? If the email passes this mental screening, most people will just open the email. But what if the bad guys can make it look like it came from a trusted source? From your Uncle Jerry or your credit card company? They may even include the last four digits of your credit card number.
The bad guys are getting good – really good at fooling you. They are not content to just send out random emails to random people, but are gathering information about you – where you work, who you communicate with, online companies where you shop, etc. How do they know about Uncle Jerry? Well, you keep posting about him on Facebook. Social media websites are literally databases of information about you, your company, your relatives and where you shop. So it is not very difficult to create a custom tailored email that includes a few nuggets of personal information to lower your defenses. And when you open that personalized email – you have been Spear Phished!
So what can you do?
The best defense is common sense. Be constantly aware of an email’s ‘red flags’. Here are a few examples of common red flags:
- If you receive a notice that your package from FedEx needs your attention, but you are not expecting something from FedEx, that should be a red flag.
- If you recognize the company or service and they may even include your account number, but the sender has an unusual or foreign email address, that should be a red flag.
- If the email has a lot of misspellings or contains very poor grammar (and is not from your 6 year old niece), that is a red flag.
- If you receive an email to reset your password but you did not initiate it, that should be a red flag. If unsure, close the email and go to the website directly through your browser, but never click on the unsolicited link.
- If the email is of an urgent nature and requests sensitive information, that is a red flag (you can always confirm with a quick phone call if it’s that urgent).
But as mentioned before, we are all human and we get tired, bored and have to go through hundreds of monotonous emails every week. It is not surprising that we miss a few of these red flag clues. If you think that you have clicked on something that you shouldn’t have, the best thing you can do is let an IT professional know and run a malware scan on your computer.
When someone tells me that they think they were hacked or they clicked on a suspicious link, I tell them that the first thing they should do is change their password. The second thing to do is run a virus scan on the machine they used to open the suspicious link.
If you think you are a victim of a phishing or spear phishing email, you can contact Infinity Networking and we will help you assess your situation.
If your business would like to know more about Security Awareness Training for its employees, Infinity Networking offers a free trial of Webroot’s Security Awareness Training with simulated phishing emails and a library of security awareness training videos.
Top Technology Concerns for 2020
The top technology concerns for 2020 will likely be important for both businesses and consumers alike. These include Cybersecurity, Privacy and more refined, targeted Ransomware. Although future articles will go into more detail about each of them, here are the basics and why you should be paying attention.
Cybersecurity
This term has been tossed around for so many years, most people cannot clearly define it but it is a commonly used catchphrase. Its origins evolved from society’s use of the prefix ‘cyber’, which in Greek has do to with steering or governance and was first popularized by a mathematician in the 1940’s with the term cybernetics. But over the years, attaching cyber- to a word makes it seem futuristic. So instead of computer security, or network security, people started using the catchy term ‘cybersecurity’. It is used to describe many aspects of computer or network security, but for more current application, it can be best described as an awareness of how we secure our use of technology to only allow access to our data to those entities whom we have granted access. In this definition, cybersecurity would encompass concepts such as password management, encryption, firewalls, network perimeter security, antivirus/anti-malware, authentication methods, etc.
Cybersecurity is not just for businesses. Computer data, both corporate and personal can be valuable to others, especially those who would exploit it. Therefore, we must be diligent in protecting our personal data as well as keeping our business data secure.
Privacy
On almost a weekly basis we hear about a new data breach at a large company that has compromised the private information of everyday people. As a society, we can only trust that when we provide personal data such as name, address, date of birth, social security numbers or credit card information, this information is kept safe from the bad guys who would use it against us. But just as diligently as we strive to protect our personal data, others are constantly working to uncover it. Although we have very little control over our data once it is in someone else’s possession, we must still be diligent about whom we give our personal information. New laws in California and the European Union now give the public certain rights to review and remove personal information that we have provided. Common sense is the best defense when protecting your personal information.
- Only give your information for legitimate reasons to verified requests.
- Only give the information that is necessary and nothing extra.
- Be cautious and feel free to question anyone requesting your personal information.
Ransomware
In 2019, ransomware cost business more than $8 billion, with an average ransomware attack cost of $133,000. One of the most widely used methods that hackers are still using to extort money from companies and individuals is with the use of targeted ransomware. By gaining access to a computer or network, usually by an email attack or an exploited network vulnerability, the files and folders of a network are locked by encryption so the users can no longer access them. Conveniently, when someone tries to open an encrypted file, a notification will appear with instructions for how to pay the hacker to decrypt and unlock their network files. The ransom payments are requested by using untraceable bitcoin transactions and in most cases, the encrypted files are unlocked successfully. If the hackers did not follow through on their promise to unlock the files, no one would pay the ransom.
As a business or individual, if this should happen to your data, your options are limited. If you are diligent with your backups, you can simply restore your data from an unencrypted date before the hackers gained access. Or, you can lose your data permanently. Or you can pay the ransom. For some companies, it is easier and more cost effective to pay the ransom and many have done just that. Of course, this does nothing to combat this illegal activity and may even be encouraging its success.
Our advice regarding Ransomware is:
- Be diligent with your email – know how to identify a phishing attack
- Employ reliable and frequent backups
- Never enter your credentials from an email request unless you are the one initiating it (password reset, e.g.)
- Keep your computer security patches up to date
If you are a victim of Ransomware:
- Disconnect the network/computer from the internet
- Stop any backups that are running (you will be backing up the infected files)
- Restore your files from backup if possible
- Try to find the point of entry for the hackers (suspicious email, open remote access) and only reconnect to the internet once the method of access has been determined or you may end up back I the same place all over again.
- Contact an IT professional for expert advice
The Infinity Networking Technology Advice Blog will be providing useful information about these topics and more through the coming year. Please sign up for notification when a new blog article is published. And if you are worried about the data you give us – here is our privacy policy.
Change Your Default Passwords
One of the most commonly overlooked security vulnerabilities on a corporate network can also be easily exploited – the Default Password. With so much emphasis about our own personal passwords; the need to frequently change them and to keep them complex and and unguessable, companies often forget that many computers, servers and network devices come pre-configured with default passwords. For example, if you order a Netgear router for your internet and WiFi connections, the device has a default username/password to configure the device of admin/password. Routers, switches and sometimes even operating systems often come with a simple login which can be easily Googled or perhaps have no password at all! A few years ago, some enterprising bad operators were using telephones to access the neglected configuration credentials of onsite phone systems.
What you can/should do:
1) If you use a in-house phone system (Panasonic, Avaya, Nortel, ShoreTel, etc.) contact your phone provider right now and ask if they have changed the default password for your system. Some of our clients discovered that their phone systems had been hacked and were making hundreds of toll calls overseas after hours on their dime!
2) If you do not know the login and password for your internet router or WiFi access point (not your WiFi password, but rather the credentials used to configure the device), find out from the person managing it if they have changed the default password.
3) Do the same with your Camera and Security systems or any other devices that can be accessed from the internet.
4) Audit your workstations and servers to make sure that the Administrator and Guest accounts are either disabled or that strong passwords have been assigned to them.
Infinity Networking can run a complimentary Network Security Scan to help you identify potential security holes in you company’s network. Contact us for you free assessment today.